Floating cities of the future, National Geographic

National Geographic, Daily News, Jul 2012
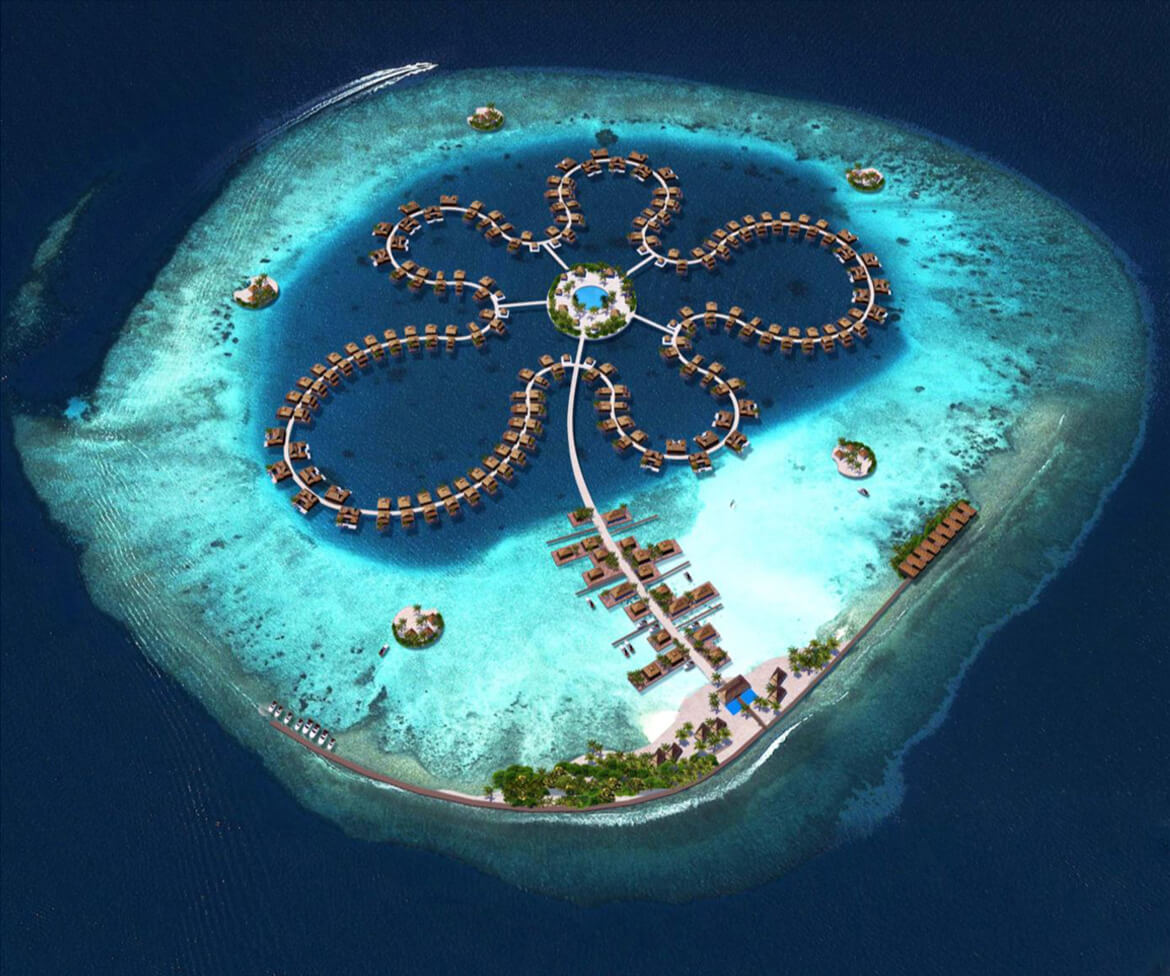
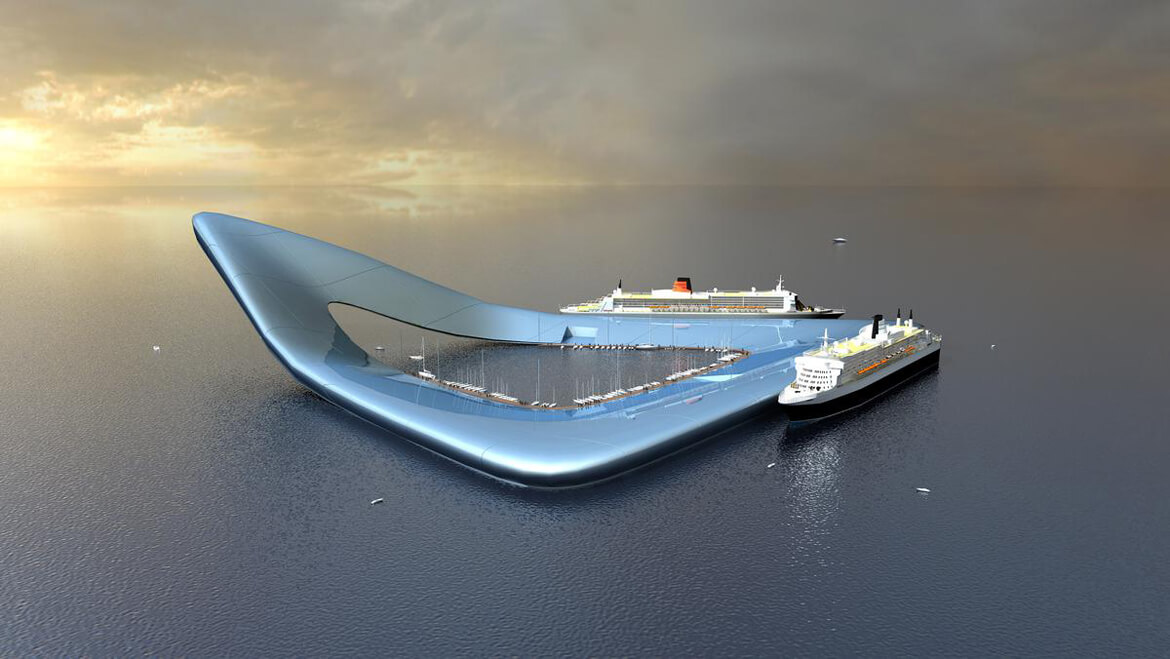
FLOATING CRUISE SHIP TERMINAL
This 5-million-square-foot (490,000-square-meter) floating cruise-ship terminal could host three large vessels while providing passengers a novel offshore experience, complete with open-ocean hotel stays, shopping, and dining, according to designers.
An inner “harbor” would allow smaller vessels to dock and would provide natural light for the interior of the terminal. Ten percent of the roof would be covered in photovoltaic cells that harvest solar power, according to Dutch architect Koen Olthuis of Waterstudio.NL.
The terminal is just a vision now, but Olthuis’s firm, which is committed to buildings that both adapt to and combat the challenges presented by climate change and sea level rise, has made other floating fantasies come to life.
Waterstudio.NL, based in the Netherlands, has worked on a floating city near The Hague and has started projects in the Maldives, China, and the United Arab Emirates.
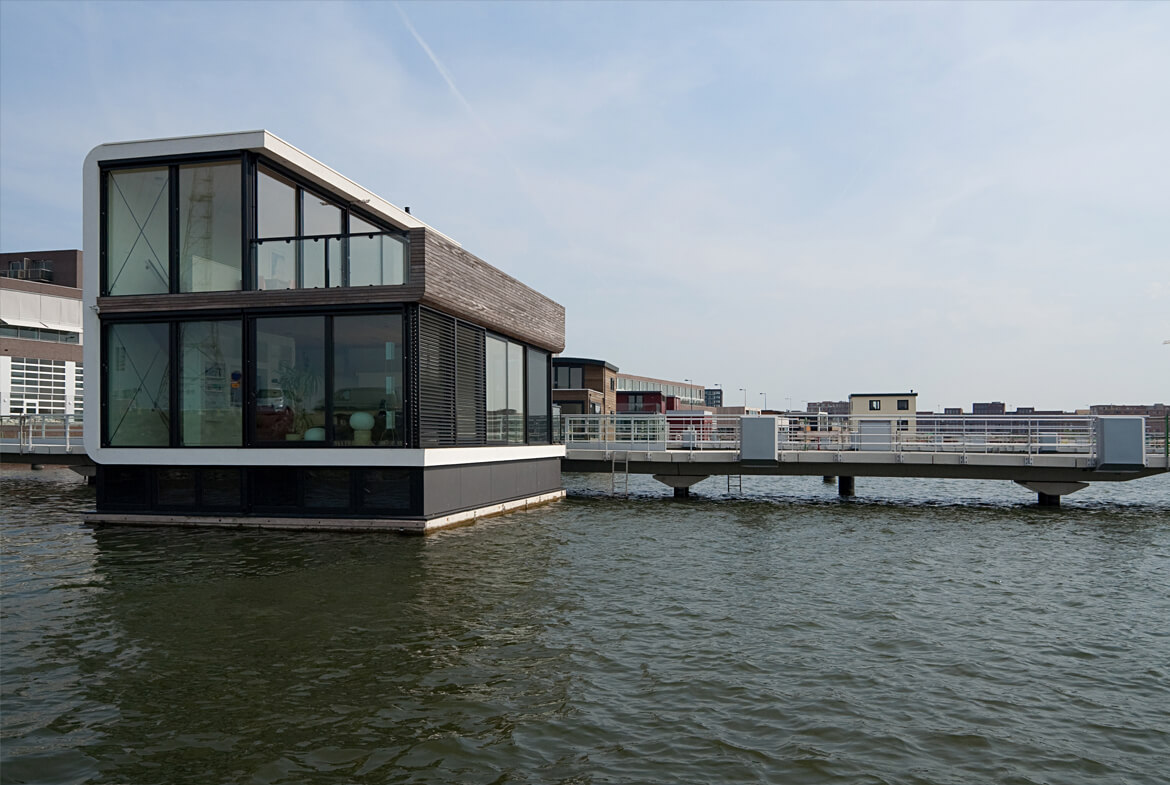

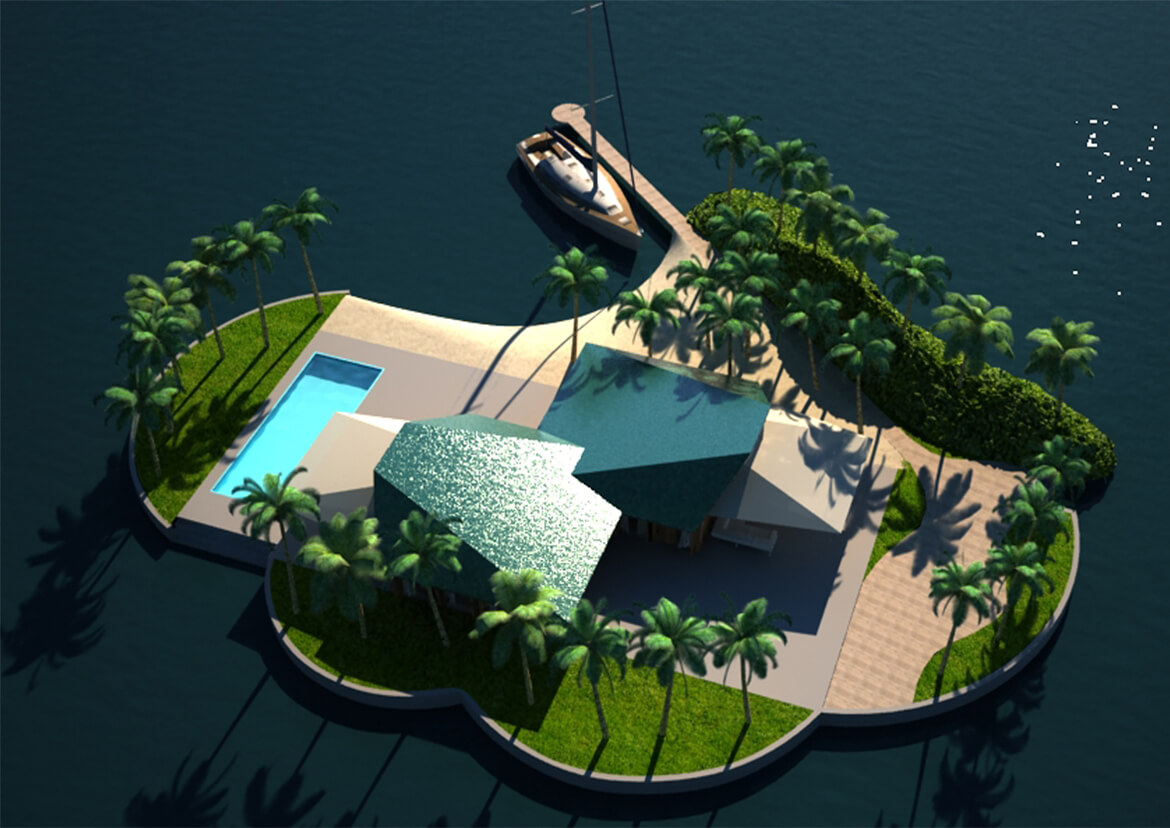
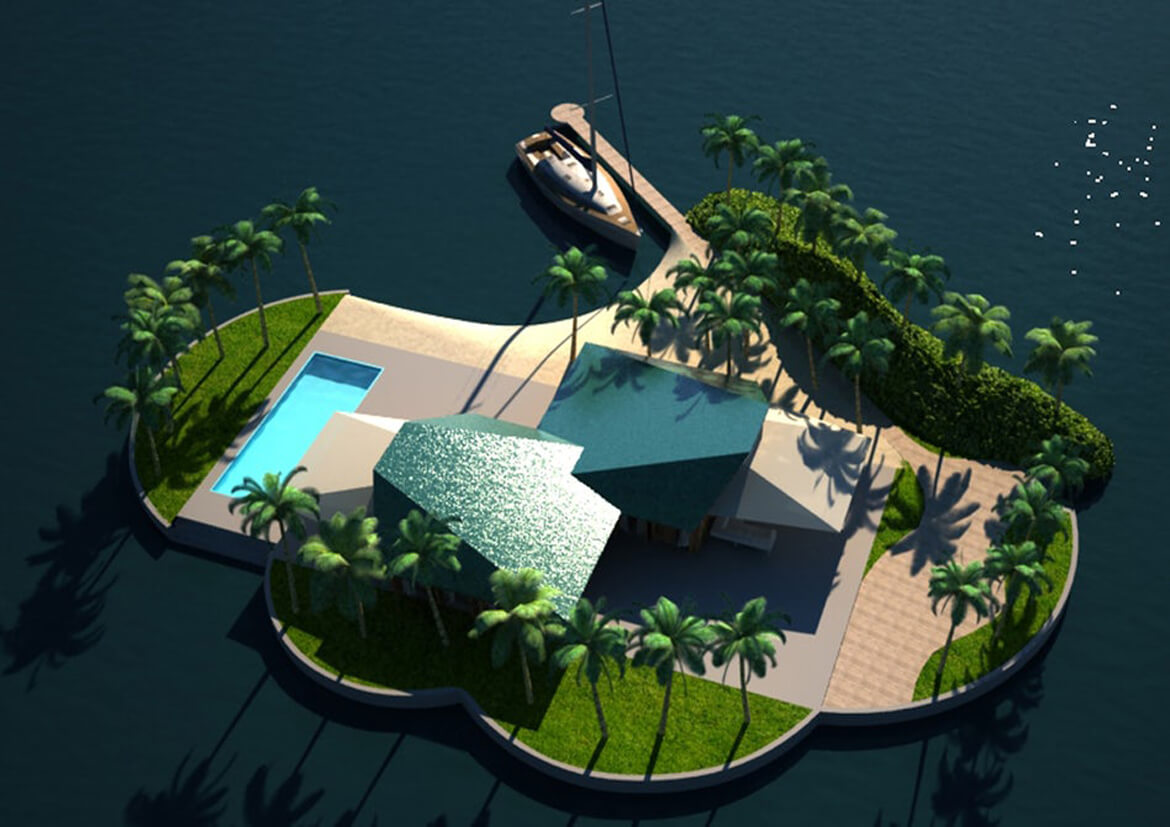
FLOAT HOUSE
Making the most of waterfront views, Dutch architect Koen Olthuis designed this floating single-family water villa in Amsterdam to maximize privacy and versatility.
Completed in 2008, the building’s bedrooms and bathroom are on the first floor, partially below water. Large sliding doors on the top floor open to a wooden deck, offering the illusion of being on a boat.
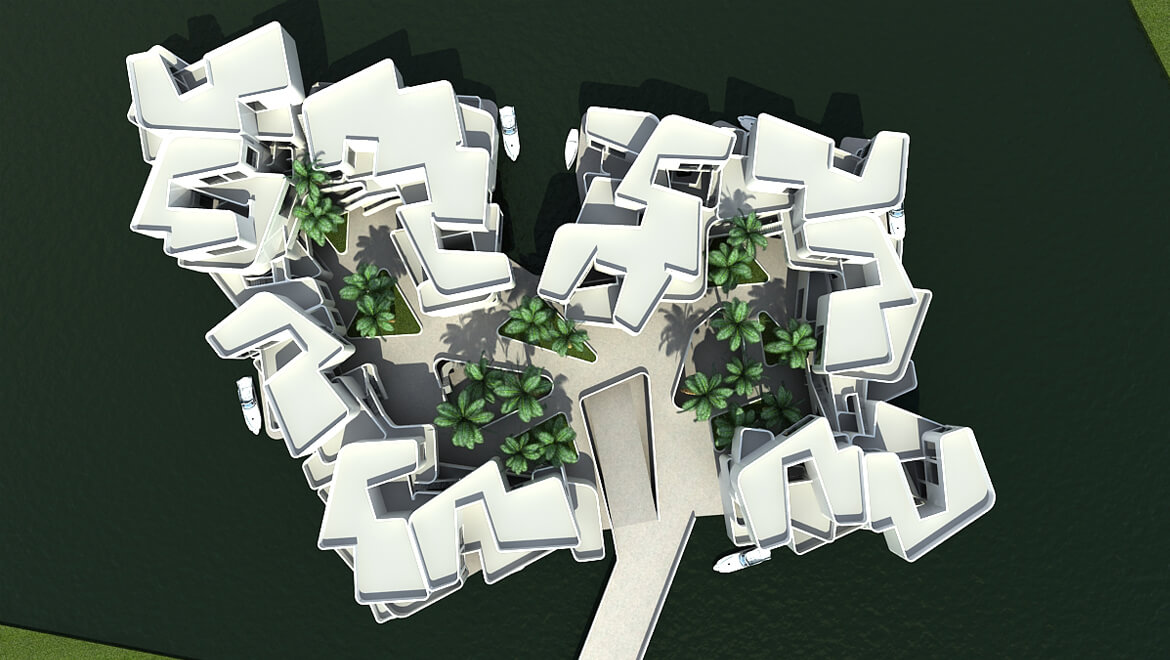

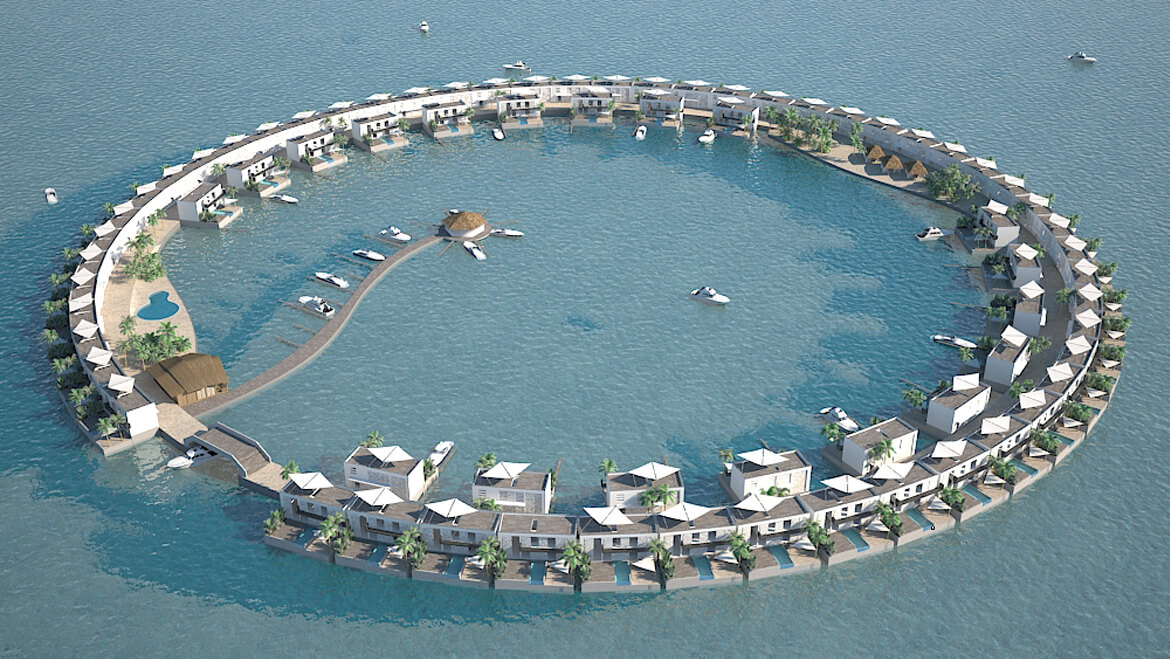
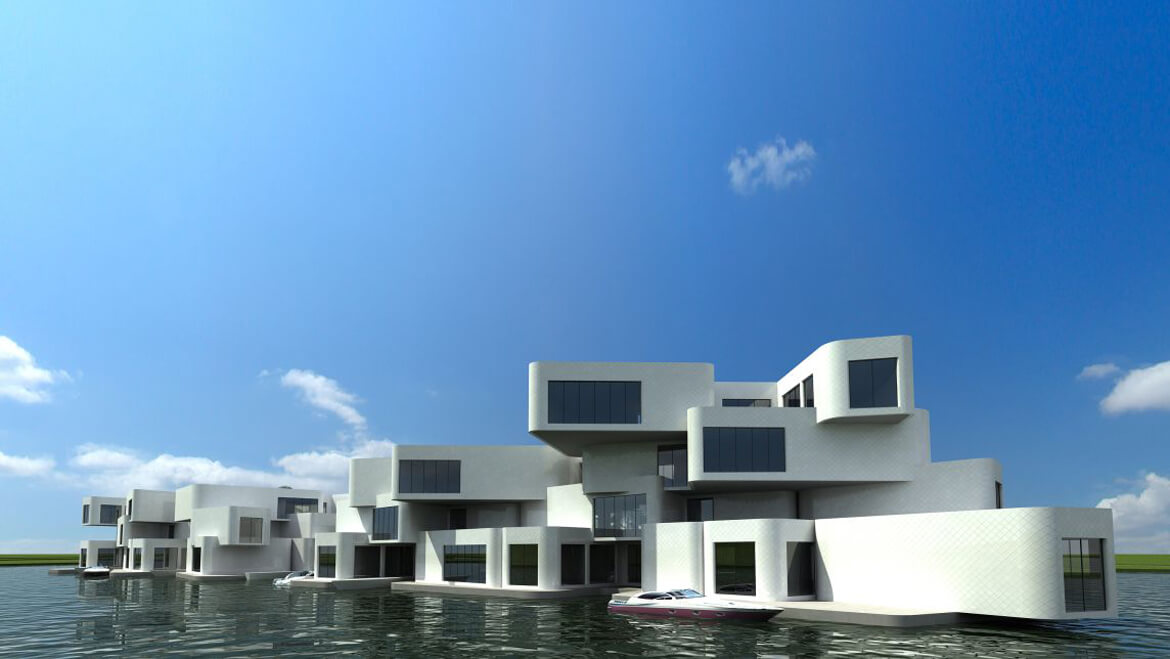
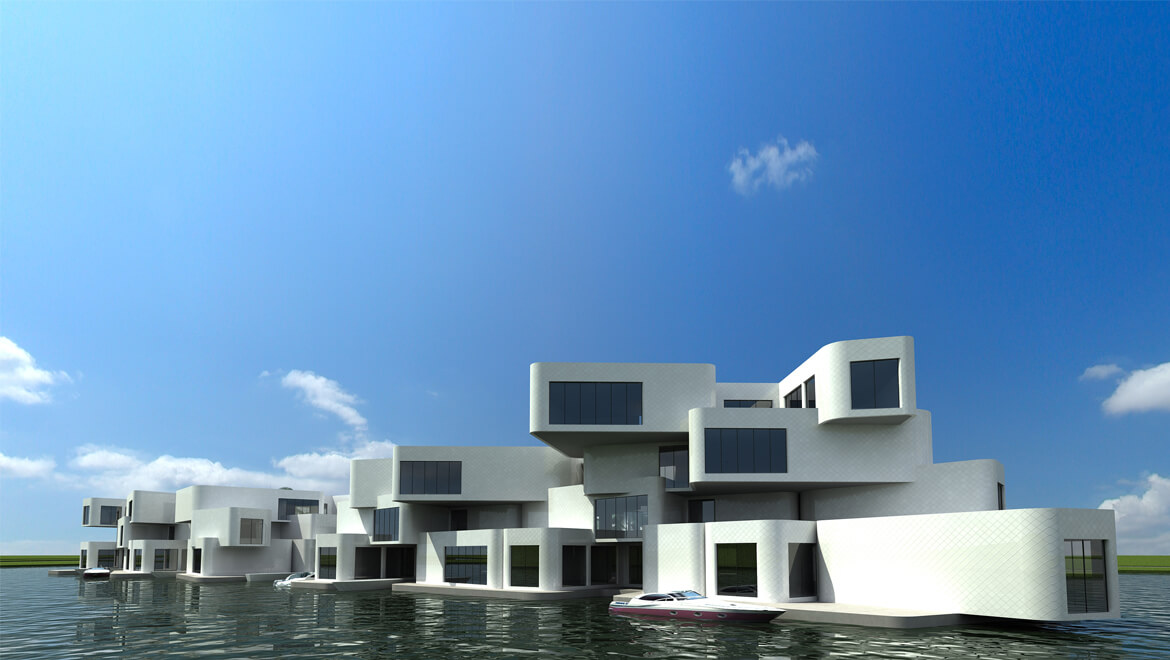
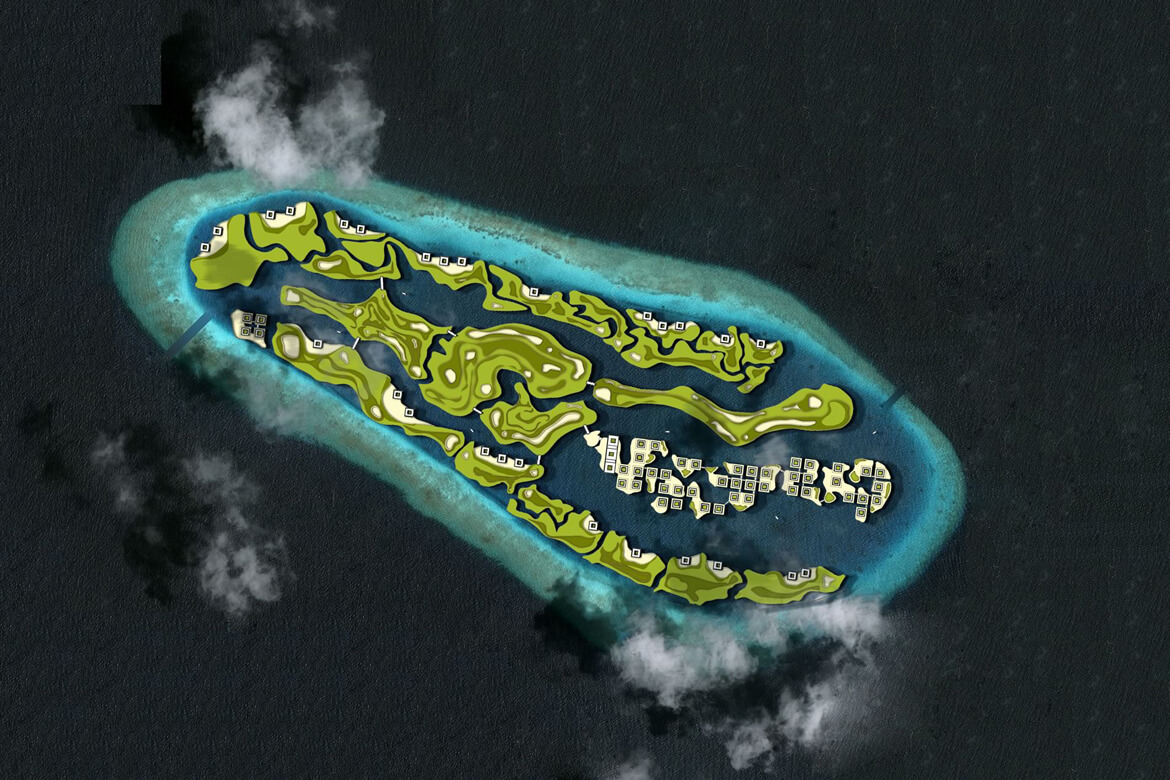
THE CITADEL
Scheduled for completion in 2014, the Citadel could be Europe’s first floating apartment building, according to architect Koen Olthuis of Waterstudio.NL. The 60-unit complex is to be built in the Dutch city of Westland, near The Hague, and is meant to protect people from flooding in a country that sits, to a large degree, below sea level.
Holland is home to more than 3,500 inland depressions, which can fill with water when it rains, when tides come in, or as seas rise overall. These so-called polders are often drained by pumps to protect residents.
Floating single-family homes are not uncommon in this soggy country, but the Citadel—to be built on a flooded polder—will be the first high-density floating residential development. The complex’s floating concrete foundation will be connected to higher ground via a floating road.
Olthuis predicts the Citadel—and its five planned neighbors—will consume 25 percent less energy over its life span than a conventional building.
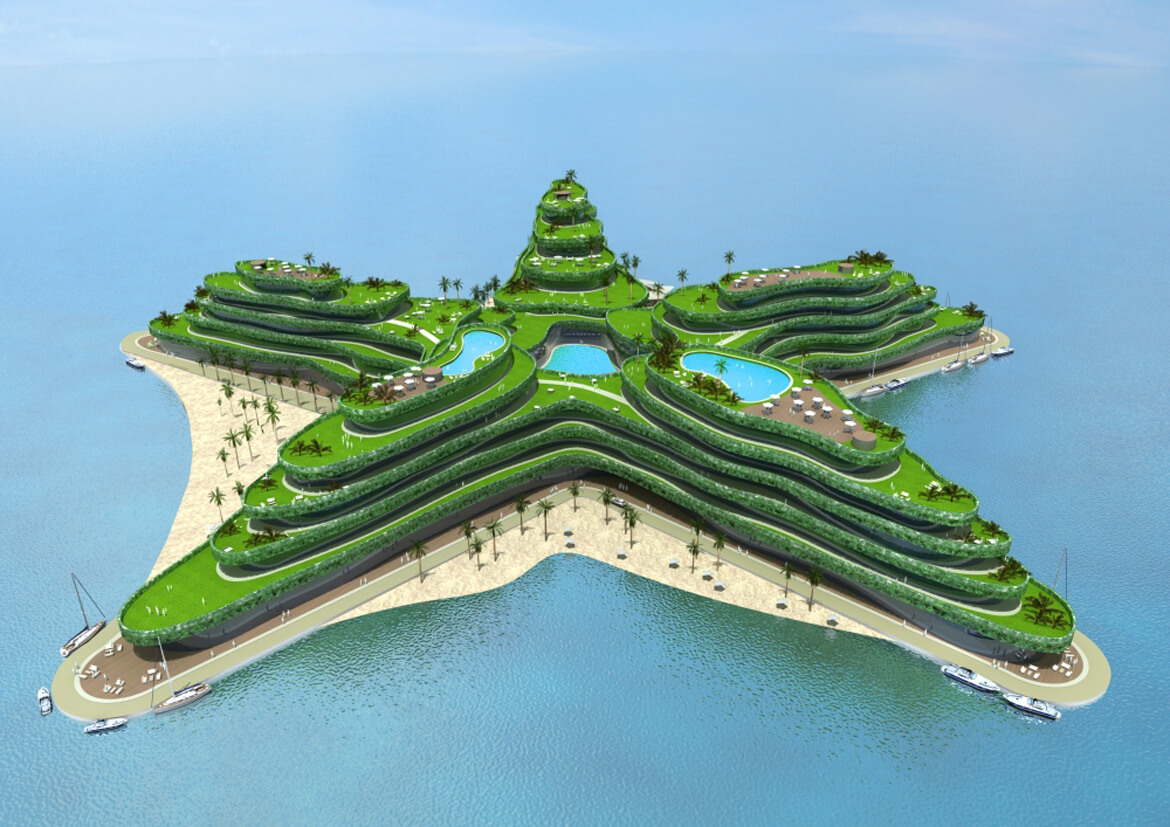

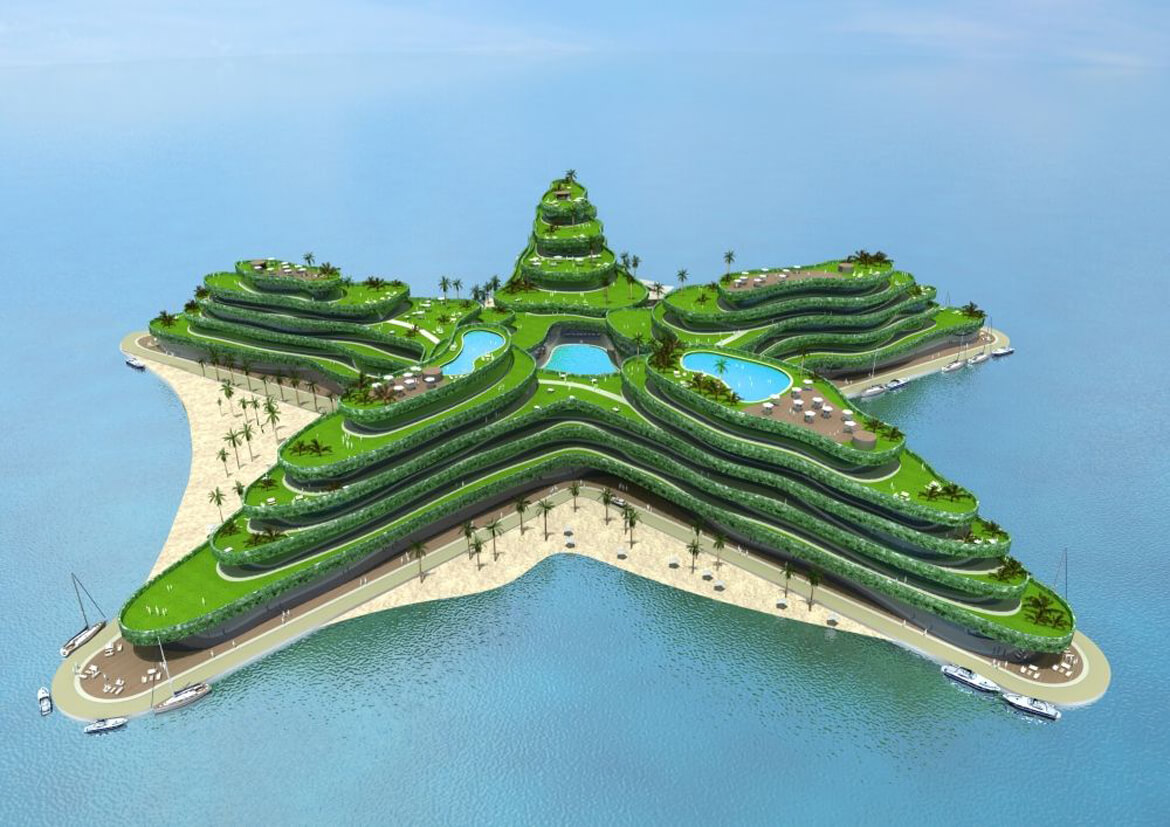
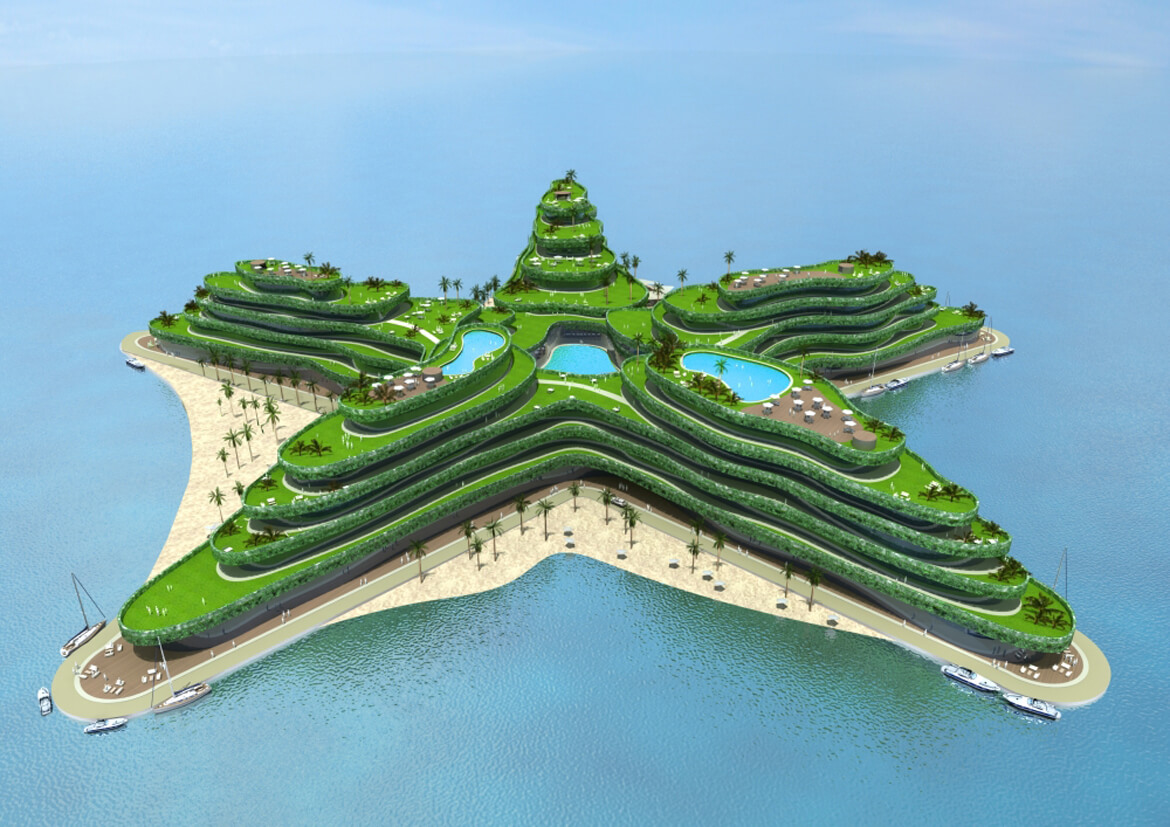
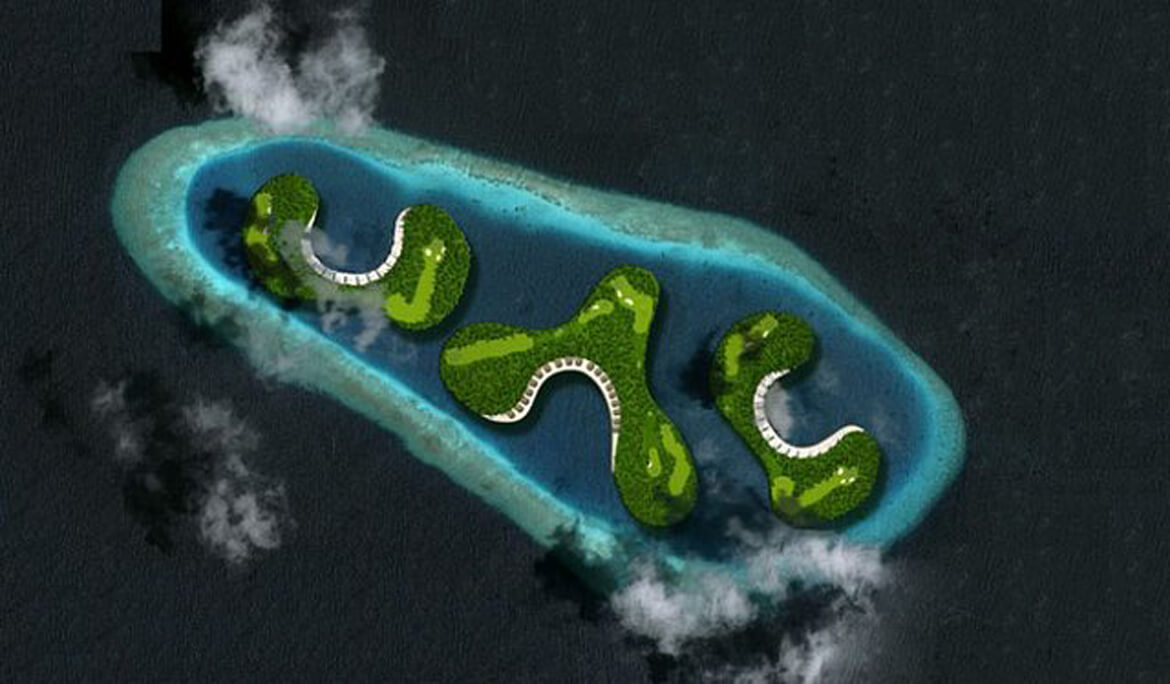
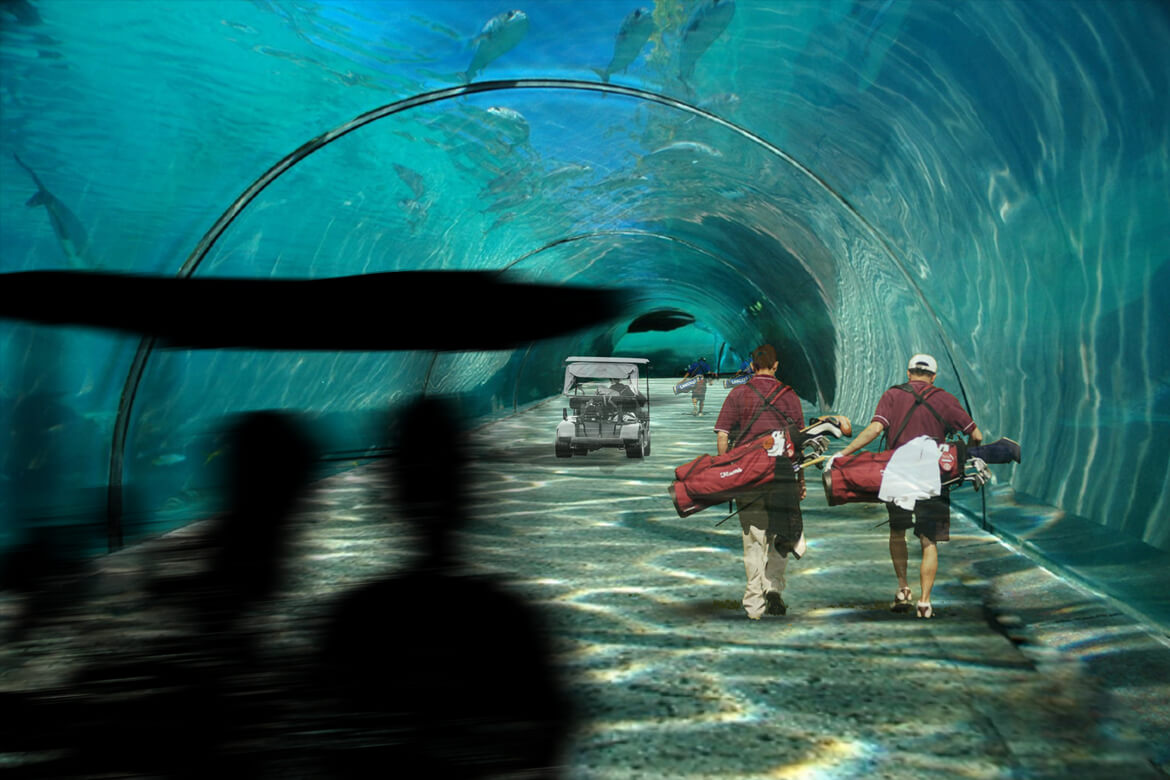
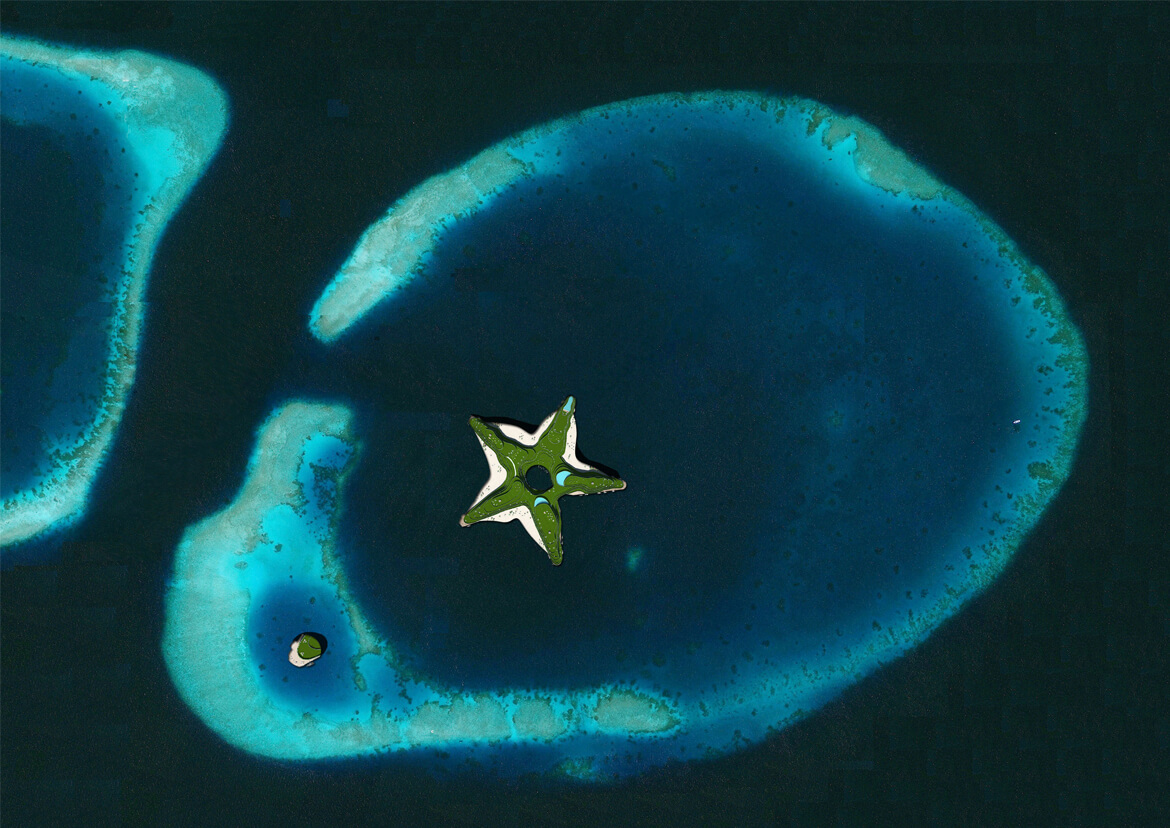
GREEN SEA STAR
Slated to open in 2014, the Greenstar is to be a floating hotel and conference center off the Maldives in the Indian Ocean. The island nation is the world’s lowest-lying country, making it among the most threatened by anticipated climate change-induced sea level rise.
Designed by Waterstudio.NL to blend in with its ocean surroundings, the Greenstar will have room for 800 overnight guests and 2,000 conference attendees.
Intended to be highly efficient, the development’s small environmental footprint is a tribute to the country’s determination to fight global warming, according to Waterstudio.NL architects. Appropriately enough, organizers intend the Greenstar to be the number one meeting place for global climate change discussions.