Biscayne Times, Erik Bojnansky, July 2014
A Dutch company has submitted plans to anchor 30 artificial floating islands in Maule Lake, a privately owned lake in North Miami Beach. Maule Lake lies east of Biscayne Boulevard, adjacent to the Aventura community of Point East, the North Miami Beach neighborhood of Eastern Shores, and the twin 24-story towers of Marina Palms Yacht Club & Residences, currently under construction at 172nd Street and the Boulevard.
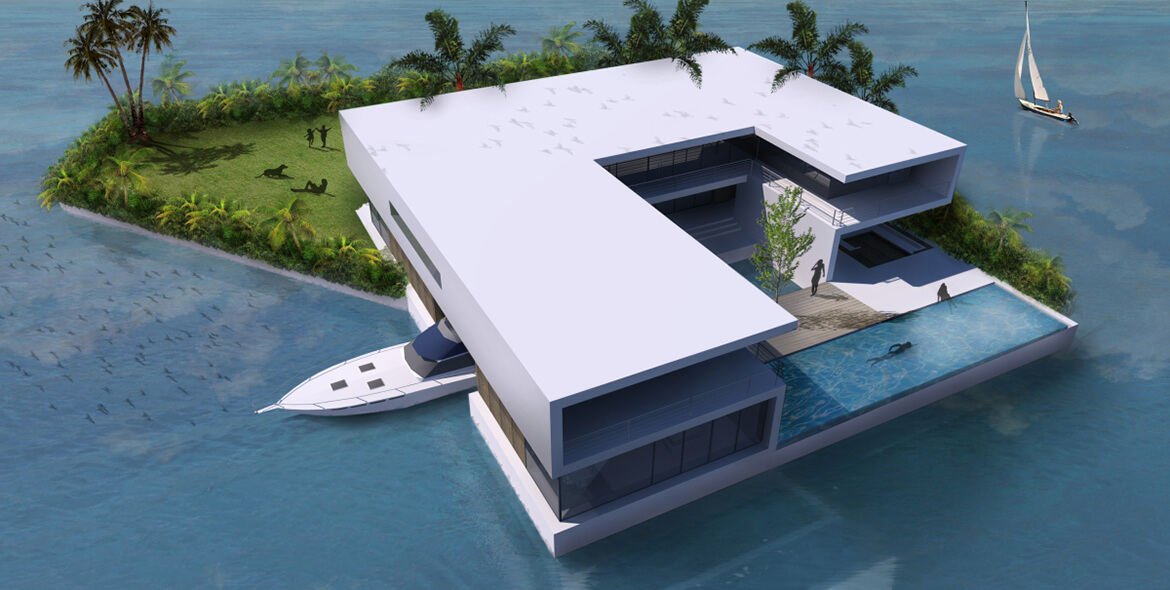
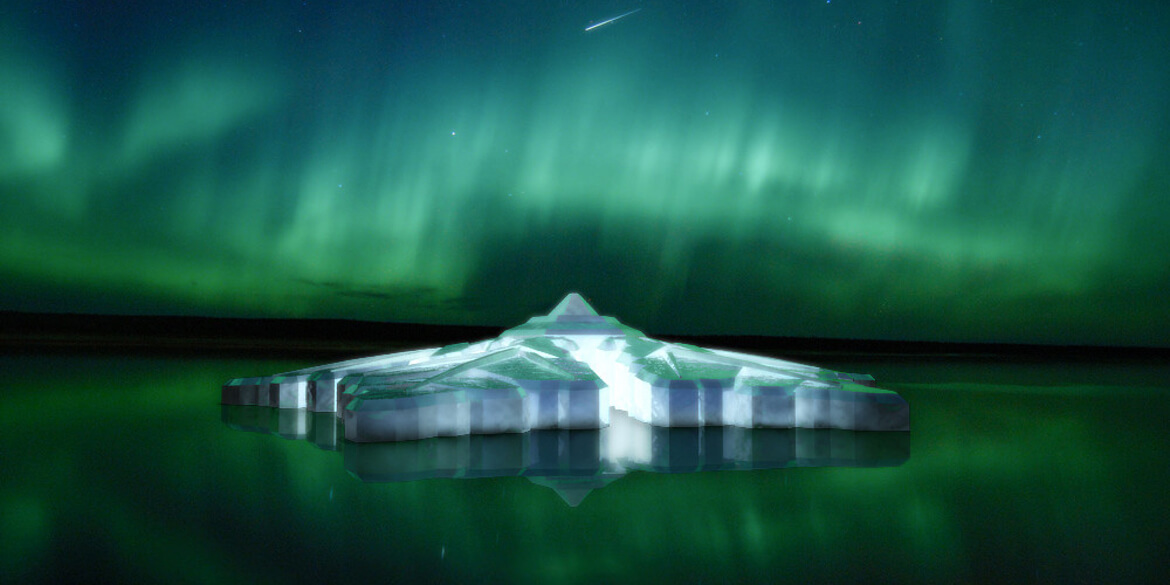
The project’s name: Amillarah Private Islands — North Miami Beach. The project’s developer: Dutch Docklands USA, a company owned by Frank Behrens, chairman of the Miami Dutch Chamber of Commerce.
Behrens didn’t return several phone calls for comment, but in August 2013, he told Miami Todaythat his company was considering a body of water somewhere in Miami-Dade County as the site to unveil Dutch Docklands’ floating-home concept in the United States.
“You can create whole new communities, and because it’s floating and on the waterfront, it would mean very high-end real estate,” he told the weekly newspaper. “You can create private beaches, private islands. Those big projects could be easily realized in Miami and would be fantastic attractions.”
Dutch Docklands, based in Delft, the Netherlands, is the parent company of Behrens’s U.S. subsidiary. The award-winning firm, which specializes in floating technologies and design, was founded in 2005 by real estate developer Paul H.T.M. van de Camp and Koen Olthuis, an architect who has made a career designing luxury homes and other floating structures via his architecture firm Waterstudio. Olthuis also has patents for floating foundations strong enough to hold dozens of homes, roadways, cars, and parks, even cruise ship terminals.
Utilizing Olthuis’s patents, Dutch Docklands is designing a floating apartment complex for South Holland, re-engineering the floating islands for Dubai’s Palm Island project, and building a series of floating projects for the Maldives. In fact, the proposed floating islands within Maule Lake are named after another Dutch Docklands project, Amillarah, in the Maldives. The word amillarah means private island in Maldivian, according to Dutchdocklands.com.
Maule Lake, with direct access to the Intracoastal Waterway and the ocean, covers 174 acres and has a deep bottom that can accommodate yachts up to 100 feet long, according to a real estate website.
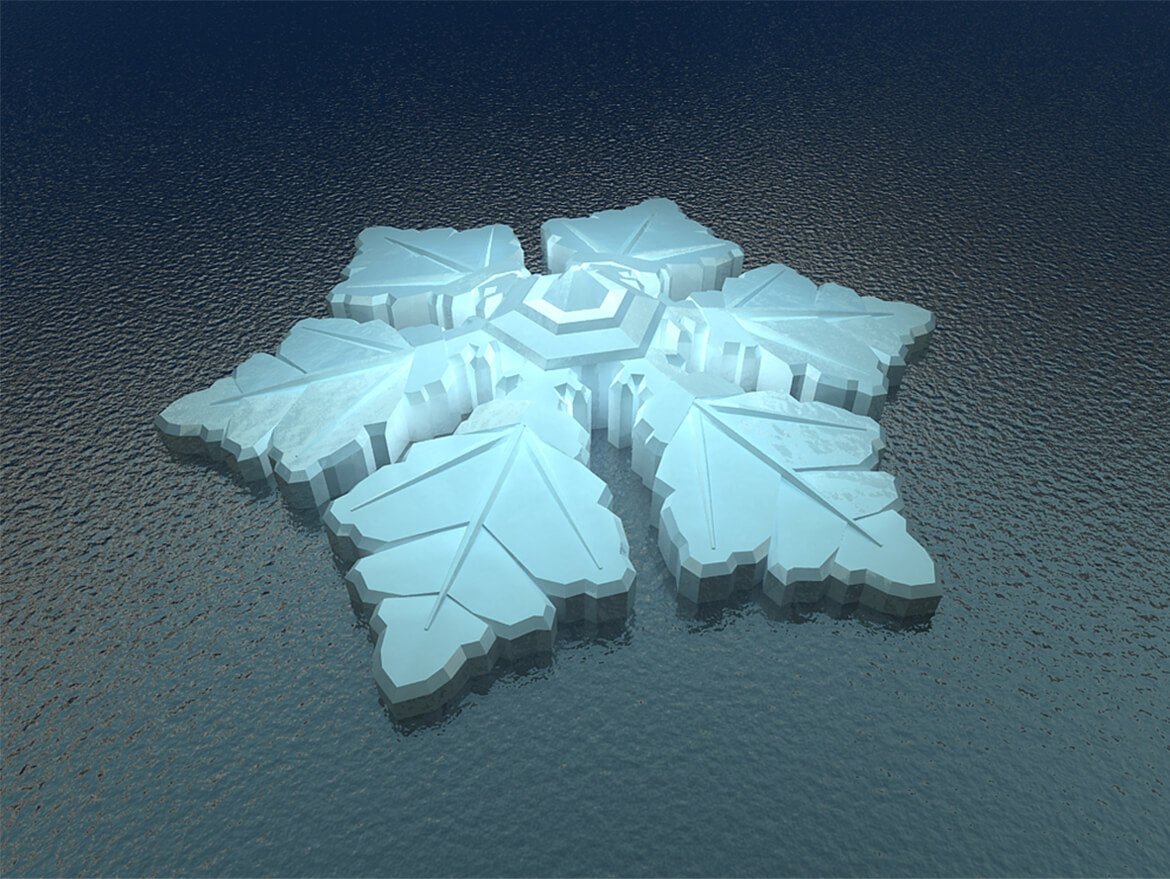
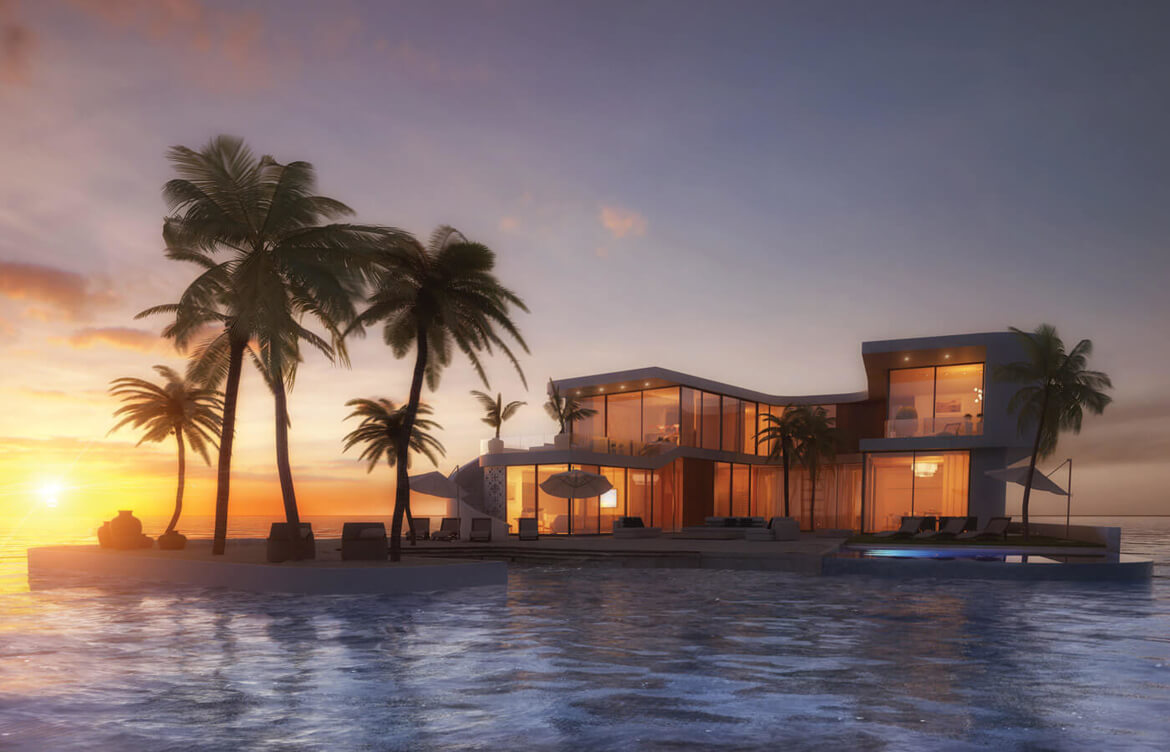
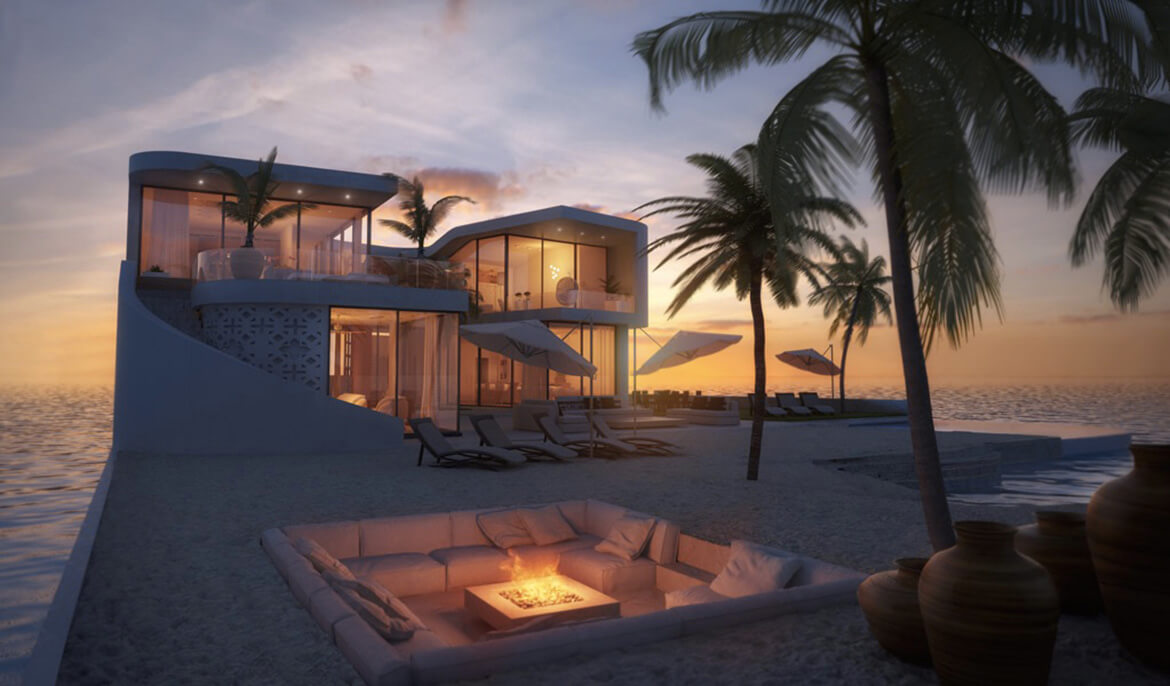
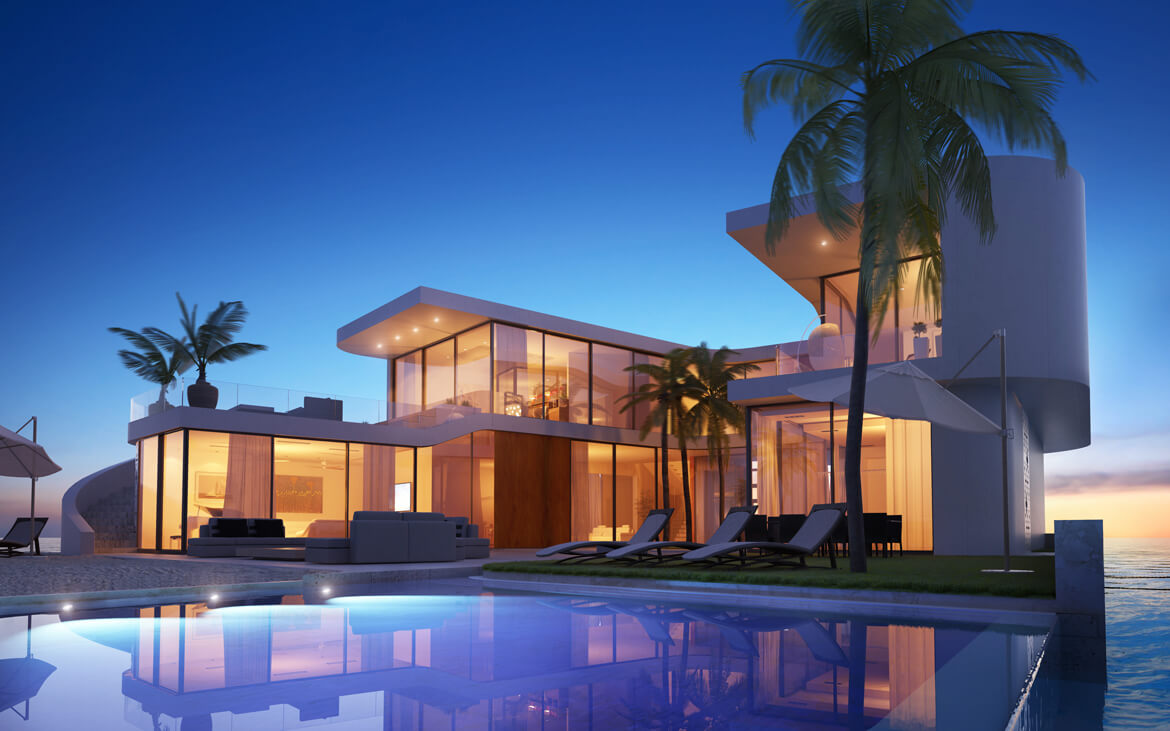
Under the plans Dutch Docklands submitted to the City of North Miami Beach on June 26, the Maule Lake version of Amillarah would consist of 29 manmade, anchored islands, each of which would include a two-story, four-bedroom villa, a patio, garden, sandy beach, swimming pool, rooftop terraces, al fresco dining areas, and two boat slips. A 30th island would be an “amenity island” staffed 24 hours a day for the exclusive use of residents and their guests.
If the project moves forward, all 30 of the islands, co-designed by Waterstudio and Coconut Grove-based Bermello Ajamil & Partners, would be constructed offsite and transported to Maule Lake.
Boats would be an essential element for the islanders: Each island would be at least 500 feet from shore and about 80 feet from its nearest neighbor.
Another interesting feature of Amillarah Private Islands: They would be off the grid.
“Dutch Docklands have designed the floating islands to be virtually self-sustaining,” according to Greenberg Traurig environmental attorney Kerri Barsh, a lobbyist for Dutch Docklands in a letter to Carlos Rivero, North Miami Beach’s acting planning director.
“By deploying cutting-edge technology and sustainable building designs, Dutch Docklands will eliminate the need for the floating islands to connect to existing potable water supplies, waste water collection systems, or to electric utilities,” her letter states.
Freshwater would be provided by “collectors and advanced filtration systems,” according to the letter. Solar panels and “hydrogen-powered generators” would provide electricity. Solid waste would be gathered by a private contractor and a special vessel “will be kept ready at all times for the exclusive use of municipal emergency responders.”
As for the disposal of human waste, each of the 6900-square-foot villa islands, and the 6800-square-foot amenity island, would be equipped with a “biological sewage facility” to “address wastewater and sewage consistent with U.S. EPA regulations.”
Perhaps the best news for a city in search of additional revenue, the letter points out, is a U.S. Supreme Court decision last year that floating homes are “akin to real property and not vessels,” and thus can be taxed. (The case was brought by North Bay Village resident Fane Lozman against the City of Riviera Beach, which demolished his houseboat.)
Since the islands will be marketed to affluent islanders who will live on Amillarah only “40 percent of the time,” there will be few, if any, floating homeowners claiming a homestead exemption.
“Assuming each residential island is appraised at a value of $12.5 million and applying 2013 millage rates,” according to Barsh’s letter, “we anticipate that the project will generate approximately $2.8 million annually in [property] tax revenue for the city.”
But for Amillarah to happen, part of Maule Lake will need to be rezoned, Barsh noted. North Miami Beach’s swath of Maule Lake is currently designated “as an open water and transportation corridor.”
Thus Barsh is asking for PUD-3 zoning for a 39-acre section of the 174-acre lake. Under PUD-3, a developer could construct up to 1941units in buildings as tall as six stories on 39 acres. With bonuses, a developer could create 2911 units in towers up to 12-stories in height on PUD-C zoned land. (Development is not permitted in Aventura’s sliver of Maule Lake, which the city refers to as a “conservation district.”)
Dutch Docklands USA still needs to close on its contract to buy the lake from a trusteeship headed by Raymond Williams, a descendant of E.L. Maule, founder of the Maule Rock Mining Company.
During the early 20th Century, 60 train carloads of limestone rock each day were mined from what is now Maule Lake, and used to construct roads, bridges, and buildings in Dade and Palm Beach counties. The limestone also served as ballast for Henry Flagler’s railroads before being replaced with granite, says local historian Seth Bramson. Maule Rock Mining wasn’t alone. Ojus Rock Mining Company, owned by A.O. Greynolds, was extracting rock from the earth just a mile west of Maule’s mine. Sometimes the competition turned nasty. In January 1921, Ojus Rock Mining took out an ad in the Miami News claiming that Maule’s rock was shoddy.
Eventually, Maule’s rock pit became a lake. “When you go down to a certain level in South Florida,” Bramson explains, “you hit water.”
Whereas Greynolds gave his rock mine to the county for Greynolds Park (see “Green Piece,” June 2013), Maule Rock Mining sold chunks of its 300 acres to real estate developers and to the state (for highways). In 1957, Maule Lake was dredged for fill for the creation of Eastern Shores.
Brackish water flows in and out of Maule Lake via Snake Creek, the Oleta River, and neighboring Dumbfoundling Bay. So, too, does aquatic life. Snook, catfish, and tarpon have been fished at Maule Lake for decades. The lake was even used in a few scenes for the hit show Flipper, according to a 1964 Miami News article.
Maule Lake was popular for boat racing, especially during the 1950s and 1960s. But in 1991 the state enacted strict speed limits at the lake to protect manatees. Between 1974 and 1993, 19 dead manatees were found in or near Maule Lake, according to the Miami Herald.
Since 1998, Patrick Killen, commercial director of Keller Williams Elite Properties, and his wife Karen, broker/owner of The Villas, LLC, have been trying to sell Maule Lake on behalf of the Williams trust. (In this pending deal, Patrick Killen is representing the potential buyer, Dutch docklands. Karen Killen represents the seller.)
A picture of Maule Lake adorns the top of Patrick Killen’s Facebook page. At one point, according to Killen, Donald Trump was under contract to buy Maule Lake so he could fill it in and build a high-rise there.
“I think most people don’t know that it’s a private lake,” Patrick Killen says. “For whatever reason, it’s not common knowledge.”
Maule Lake is not only private, it is pricey. Four years ago the asking price was $17 million. More recently it was listed at $19.5 million, says Killen.
Maule Lake will be a nice fit for Amillarah, explained Barsh in her letter to the city. The lake’s depth of 22 feet means it’s unlikely that “sensitive environmental resources” will be present at the bottom. Then there’s the fact that North Miami Beach and Maule Lake happen to be in South Florida.
“No place in the United States is as vibrant and exciting as South Florida,” Barsh notes in her letter. And no place in the U.S. is as threatened by sea-level rise, she adds.
In as few as 50 years, low-lying areas, such as Eastern Shores, Keystone Point, and Sans Souci Estates, may be regularly flooded during high tide. (See “Lost in a Rising Sea,” September 2012.)
For this reason, Amillarah is not just a quirky, alternative lifestyle — it’s also the future of development in South Florida, according to Barsh, writing that “Dutch Docklands believes its technology will help address some of the threat of sea-level rise. By choosing North Miami Beach for its first project in the United States, Dutch Docklands hopes its approach can become a model for the whole of South Florida and the world.”
Whatever Dutch Docklands’ intention, Marina Palms developer Neil Fairman can’t help but like the company’s top executives. Fairman says he met them a few months ago and was struck by their agreeable demeanor. Among other things, they assured him that their project won’t interfere with the operation of Marina Palms’s 112-slip marina.
“They seem like nice people, and they seem very soft-spoken and ready to cooperate with the community,” he says. As for the project itself, Fairman says, “I think it’ll be very cool.”
Click here for the website